容器
部分转载,原文
Collection和Map接口
ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、TreeMap、ConcurrentHashMap、HashTable
HashSet
集合
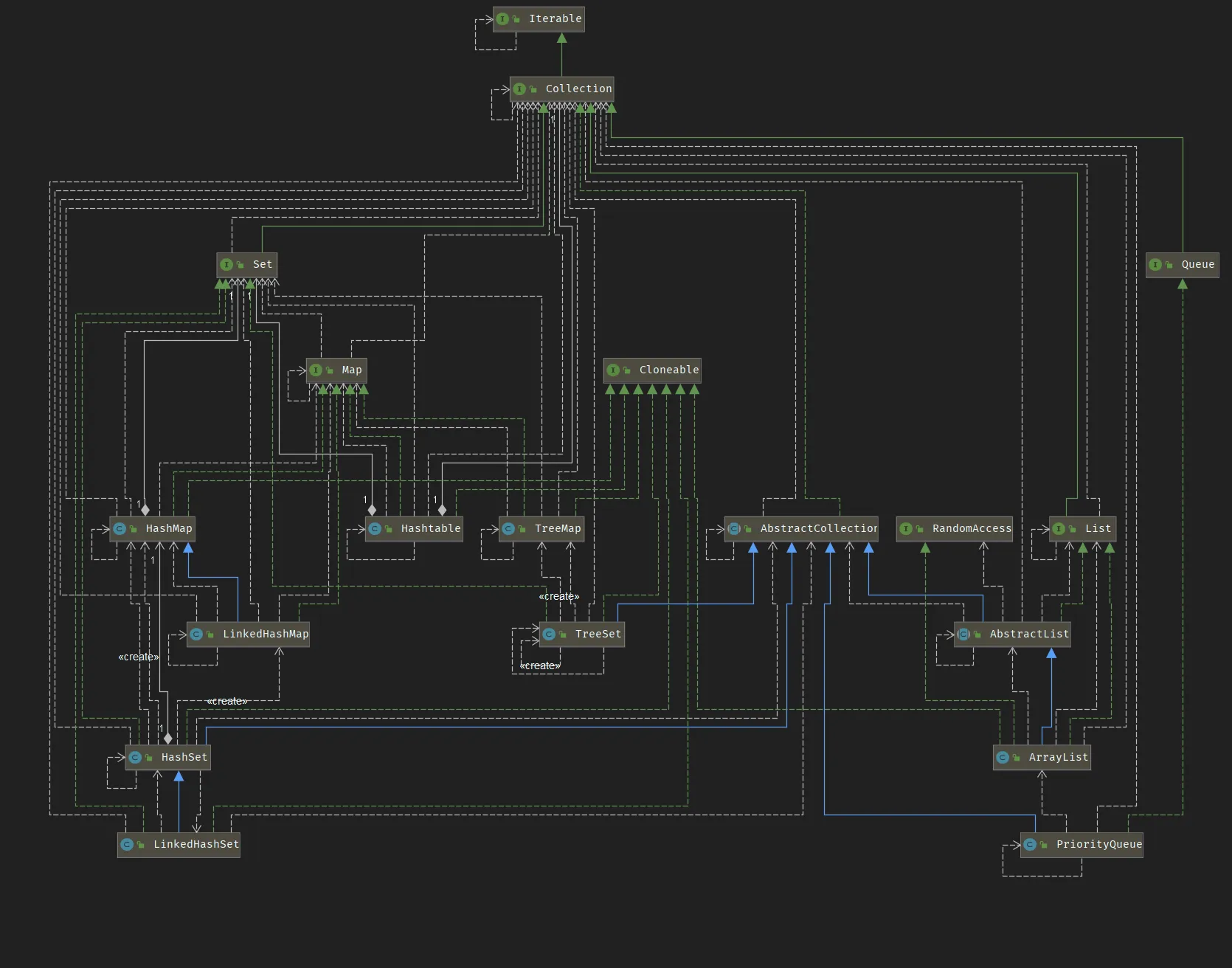
List
ArrayList
基于数组实现
适合读频繁操作
- 概览
基于数组实现,所以支持快速访问。RandomAccess接口标识该类支持快速随机访问。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable默认大小为10
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;- 扩容机制
- 添加元素的时候首先会通过 ensureCapacityInternal(size+1) 方法保证容量足够
- 如果不够则会通过 grow 方法进行扩容,新的容量为 oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1),即oldCapacity + (oldCapacity / 2)。其中 **oldCapacity >> 1 **需要取整,所以容量大概是1.5倍左右。
- oldCapacity 为偶数就是1.5倍,为奇数就是1.5 倍 - 0.5
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}- 删除元素
- 调用的 **System.arraycopy() **方法,将需要删的元素的 **index + 1 **后面的元素都向前复制一位。时间复杂度为 O(N)。
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}- 序列化
- ArrayList 基于数组实现,并且具有动态扩容特性,不一定每一位都有值填充,所以没必要全部序列化。
- **transient:**此关键字标志此属性不被序列化,被此关键字修饰的字段,只会作用于内存,不会序列化到磁盘。
transient Object[] elementData;- ArrayList 实现了 writerObject() 和 readObject() 用于控制只序列化有值填充的部分。
- 一般的读取流程
- 创建 InputStream;
- ObjectInputStream,并传入 InputStream;
- 然后调用 ObjectInputStream 对象的 readObject() 方法从 InputStream 读取对象状态信息;
/**
* Reconstitute the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance from a stream (that is,
* deserialize it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in capacity
s.readInt(); // ignored
if (size > 0) {
// be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity
int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size);
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity);
ensureCapacityInternal(size);
Object[] a = elementData;
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
a[i] = s.readObject();
}
}
}- 一般的写入流程
- 创建 OutputStream;
- ObjectOutputStream,并传入 OutputStream 输出流对象;
- 然后调用 ObjectOutputStream对象的 writerObject() 方法将对象信息写入 OutputStream;
/**
* Save the state of the <tt>ArrayList</tt> instance to a stream (that
* is, serialize it).
*
* @serialData The length of the array backing the <tt>ArrayList</tt>
* instance is emitted (int), followed by all of its elements
* (each an <tt>Object</tt>) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}- 序列化
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
oos.writeObject(list);- Fail-Fast
快速失败机制,是 Java 集合中的一种错误检查机制。当迭代集合过程中发现该集合的结构发送改变时,就有可能触发 Fail-fast,即抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 异常。Fail-fast 并不能保证非同步状态下修改一定会抛出异常,它只是尽最大努力去抛出,所以这一机制仅用于检测 bug。
如果一定要边遍历边移除,使用 Iterator
- modCount 用来记录 ArrayList 结构发生变化的次数(结构发生变化指添加或删除元素,或是调整内部数组的大小,修改元素值不算发生变化)
- 在进行序列操作时候,需要比较前后的 **modCount **是否一致,如果不一致则抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。
- 申请一个同步的 List
Collections.synchronizedList();List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArray();LinkedList
基于双向链表实现
只能顺序访问,但是插入和删除效率高
可用作栈队列
- 概览
- Node 数据结构
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}- 双向链表
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;- 与 ArrayList 比较
ArrayList基于动态数组,LinkedList 基于双向链表
- 前者支持随机访问,但插入和删除代价高,需要移动大量元素;
- 后者不支持随机访问,但是插入删除效率高;
Vector
类似 ArrayList,但是线程安全
- 同步
- 结构和 **ArrayList **类似,但是通过 **synchronized **进行同步;
- 与 ArrayList 比较
- Vector 是同步的,开销比 **ArrayList **大,访问速度慢。最好使用 ArrayList 而不是 Vector,因为同步操作可以由程序控制;
- 扩容机制不一样,默认两倍,也可以通过构造方法控制,而 ArrayList 是1.5倍;
- 扩容
- **Vector **的构造函数可以传入 capacityIncrement 参数,它的作用是在扩容时使容量 **capacity **增长 capacityIncrement。如果这个参数值小于等于0,则每次扩容 capacity 的两倍;
- 空参构造函数调用了 Vector(int initialCapacity),传入默认值10,并调用 Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) 同时设置 capacityIncement 为0;
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* capacity increment.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @param capacityIncrement the amount by which the capacity is
* increased when the vector overflows
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* with its capacity increment equal to zero.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* with its capacity increment equal to zero.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array
* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is
* zero.
*/
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array
* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is
* zero.
*/
public Vector() {
this(10);
}private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}CopyOnWriteArrayList
java.util.concurrent
同步
- 适合读多操作
- 内存消耗大
- 数据不一致,可能新数据还未同步到数组中
不适合内存敏感和实时性高的场景
- 读写分离
- 写操作在一个复制的数组上进行,读操作还是在原始数组中进行,读写分离
- 写操作加锁
- 写操作结束后把数据指向新的复制数组
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] elements = getArray();
int len = elements.length;
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
final void setArray(Object[] a) {
array = a;
}private E get(Object[] a, int index) {
return (E) a[index];
}Set
HashSet
基于Hash表实现,支持快速查询,无序。
TreeSet
基于红黑树实现,继承接口SortedSet,有序。
LinkedHashSet
基于双向链表维护的Hash表,快速查询。
Queue
LinkedList
可用作队列
PriorityQueue
基于堆结构实现,实现优先队列?
ArrayBlockingQueue
java.util.concurrent
LinkedBlockingQueue
java.util.concurrent
PriorityBlockingQueue
java.util.concurrent
SynchronousQueue
java.util.concurrent
DelayQueue
java.util.concurrent
Stack
Map
HashMap
- 1.7:基于 Hash 表和单链表
- 1.8:基于 Hash 表和链表+红黑树(当链表长度超过 8 时,会转换为红黑树)
扩容
默认扩容因子是 0.75,也就是会浪费四分之一的空间,0.75 它是一个时间于空间平衡的一个值,每次扩容两倍
线程安全
多线程同时写入,同时执行扩容操作,多线程扩容可能死锁、丢数据;可以对HashMap 加入同步锁
Collections.synchronizedMap(hashMap),但是效率很低,因为该锁是互斥锁,同一时刻只能有一个线
程执行读写操作,这时候应该使用ConcurrentHashMap。
JDK 1.7
维护了一个 Entry[] 的数组 table,Entry 存储键值对,且是一个单向链表。及数组中的每一个位置被当成了一个桶(拉链),采用拉链法解决 Hash 冲突,同一个链表中存放的是哈希值和散列桶取模运算结果相同的 Entry。
transient Entry[] table;static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o;
Object k1 = getKey();
Object k2 = e.getKey();
if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) {
Object v1 = getValue();
Object v2 = e.getValue();
if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue());
}
public final String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
}- 插入
- 默认大小为16
- 计算 key 的 Hash 值,对其区域数组长度 16,则存入取余后的位置,如果当前位置没有值,则直接存入,如果有值,则通过头插法,插入改节点。
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 键为 null 单独处理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
// 确定桶下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 先找出是否已经存在键为 key 的键值对,如果存在的话就更新这个键值对的值为 value
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 插入新键值对
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}因为 HashMap 允许存放 null 值,但是 null 无法调用 hashCode 方法,无法确定通下标,则强制通过第0个通存放键为 null 的键值对。
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 头插法,链表头部指向新的键值对
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}- 确定桶下标
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);- 计算 Hash 值
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}- 取模
令 x = 1 << 4,即 x 为 2 的 4次方
- 扩容
JDK 1.8
从 JDK 1.8 开始,一个桶存储的链表长度大于等于 8 时会将链表转换为红黑树。
当链表长度小于 6 的时候会退化成链表
TreeMap
基于红黑树实现
LinkedHashMap
通过双向链表维护元素之间的关系
LRU
- 存储结构
- 继承自 HashMap
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>- 内部维护一个双向链表,从来维护插入顺序或者LRU顺序
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;- 由 accessOrder 决定是顺序,默认false,此时维护的是插入顺序
final boolean accessOrder;- 维护顺序函数,它会在 put get方法中调用
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { }
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { }- afterNodeAccess:当一个节点被访问时,如果 accessOrder 为 true,则会将该节点移动到链表尾部。也就指定了为 LRU 顺序以后,在每次访问一个节点时,会将节点移动到尾部,则头部就是最久未使用节点。
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}- afterNodeInsertion:
- 在 put 操作后,当 removeEldestEntry 方法返回 true 时,则会移除最久未使用节点
- evict 只有在构建 Map 的时候才为 false,在这里为 true
- removeEldestEntry 默认返回 false,如果需要实现实现 LRU 缓存需要基础覆盖这个方法,这样就可以实现热点数据
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}- LRU 实现
class LRUCache<K, V> extends LinkedHashMap<K, V> {
private static final int MAX = 3;
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return size() > MAX;
}
LRUCache() {
super(MAX, 0.75f, true);
}
}- 添加
尾插法
WeakHashMap
Hashtable
和HashMap类似,但是它线程安全。不推荐使用
ConcurrentHashMap
java.util.concurrent
- JDK 1.7 分段锁 Segment
- 使用分段锁 Segment,它继承自重入锁 ReentrantLock,并发度和 Segment 数量相等
- JDK 1.8 Node数组 + 链表 + 红黑树
- CAS,在 CAS 操作失败时候使用内置锁 synchronize
JDK 1.7
- 存储结构
- 采用分段锁 Segment,每个锁维护着几个桶 HashEntry,多个线程可以同时访问不同分段锁上的桶。
final Segment<K,V>[] segments;
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;
static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;
transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table;
transient int count;
transient int modCount;
transient int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
}- 并发级别
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;- size()
- 每个 Segment 维护着一个 count
/**
* The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks
* or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.
*/
transient int count;- 在进行 size() 时,会遍历所有的 Segment 把 count 累加起来,
- 首先执行不会加锁,如果两次操作结果一致则认为这结果是正确的(尝试次数由 RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK 定义)
- 如果重试三次,就需要对每个 Segment 加锁
/**
* Number of unsynchronized retries in size and containsValue
* methods before resorting to locking. This is used to avoid
* unbounded retries if tables undergo continuous modification
* which would make it impossible to obtain an accurate result.
*/
static final int RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK = 2;
public int size() {
// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to
// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
int size;
boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bits
long sum; // sum of modCounts
long last = 0L; // previous sum
int retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retry
try {
for (;;) {
// 超过尝试次数,则对每个 Segment 加锁
if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation
}
sum = 0L;
size = 0;
overflow = false;
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {
Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);
if (seg != null) {
sum += seg.modCount;
int c = seg.count;
if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)
overflow = true;
}
}
// 连续两次得到的结果一致,则认为这个结果是正确的
if (sum == last)
break;
last = sum;
}
} finally {
if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();
}
}
return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;
}JDK 1.8
采用Node + CAS + Synchronized来保证并发安全进行实现
synchronized只锁定当前链表或红黑二叉树的首节点,这样只要hash不冲突,就不会产生并发
扩容:多线程扩容
size()方法的优化:
- CAS 累计
- 数组维护
ConcurrentCache
java.util.concurrent