设计模式
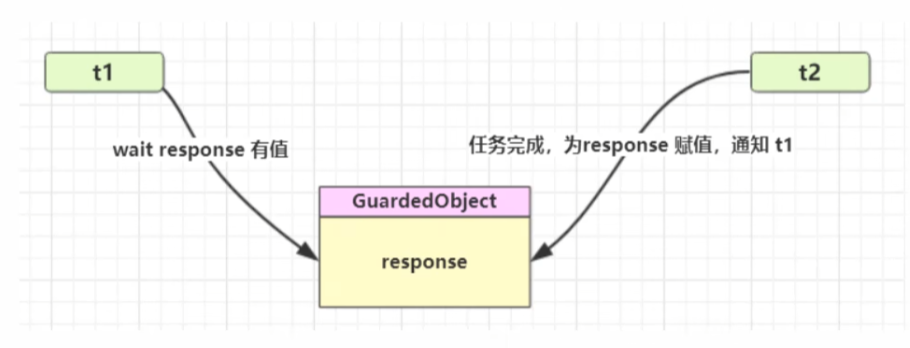
设计模式-保护性暂停
即Guarded Suspension,用在一个线程等待另一 个线程的执行结果
- 有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一 个线程,让他们关联同一一个GuardedObject
- 如果有结果不断从一个线程到另-一个线程那么可以使用消息队列(见生产者消费者)
- JDK中,join的实现、Future的实现,采用的就是此模式
- 因为要等待另一一方的结果,因此归类到同步模式
java
class GuardedObject {
private Object response;
public Object get() {
return get(0);
}
public Object get(long timeout) {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
long passed = 0;
synchronized (this) {
while (response == null) {
// 防止虚假唤醒
long waitTime = timeout - passed;
if (waitTime <= 0) {
break;
}
try {
this.wait(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
passed = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
}
return response;
}
}
public void complete(Object obj) {
synchronized (this) {
this.response = obj;
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}java
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
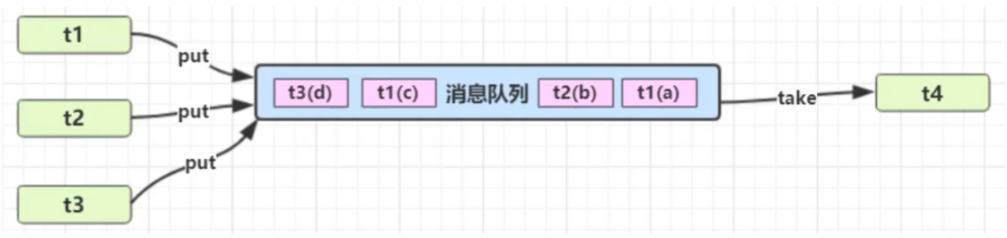
}异步模式-生产者/消费者
- 与前面的保护性暂停中的GuardObject不同,不需要产生结果和消费结果的线程一-对应
- 消费队列可以用来平衡生产和消费的线程资源
- 生产者仅负责产生结果数据,不关心数据该如何处理,而消费者专心处理结果数据
- 消息队列是有容量限制的,满时不会再加入数据,空时不会再消耗数据
- JDK中各种阻塞队列,采用的就是这种模式
java
@ToString
final class Message {
private final int id;
private final String message;
public Message(int id, String message) {
this.id = id;
this.message = message;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}java
@Slf4j(topic = "c.MessageQueue")
class MessageQueue extends LinkedList<Message> {
private int capacity;
public MessageQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public Message take() {
Message message = null;
synchronized (this) {
while (this.isEmpty()) {
log.debug("queue is empty");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
message = this.removeFirst();
this.notifyAll();
}
return message;
}
public void put(Message message) {
synchronized (this) {
while (this.size() >= this.capacity) {
log.debug("queue is full");
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("qut ");
this.addLast(message);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}java
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MessageQueue queue = new MessageQueue(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int finalI = i;
new Thread(() -> {
queue.put(new Message(finalI, "value" + finalI));
}, "producer" + i).start();
}
new Thread(() -> {
while (true){
log.info("" + queue.take());
}
}, "consumer").start();
}同步模式-固定运行顺序
wait notify
pack & unpack
同步模式-交替输出
wait notify
题目:三个线程 分别依次打印 abc 因为线程的调度是随机的,所以通过等待标记,标记下一轮的输出结果
java
public class SyncModel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WaitNotify waitNotify = new WaitNotify(1, 5);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
waitNotify.print("a", 1, 2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "a").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
waitNotify.print("b", 2, 3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "b").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
waitNotify.print("c", 3, 1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "c").start();
}
}
@Slf4j
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class WaitNotify {
public void print(String str, int waitFlag, int nextFlag) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < this.loopNumber; i++) {
synchronized (this) {
while (flag != waitFlag) {
this.wait();
}
log.info(str);
this.setFlag(nextFlag);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
}
private int flag;
private int loopNumber;
}await & signal
java
public class SyncModel2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AwaitSignal awaitSignal = new AwaitSignal(5);
Condition a = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition b = awaitSignal.newCondition();
Condition c = awaitSignal.newCondition();
new Thread(() -> awaitSignal.print("a", a, b), "a").start();
new Thread(() -> awaitSignal.print("b", b, c), "b").start();
new Thread(() -> awaitSignal.print("c", c, a), "c").start();
awaitSignal.lock();
try {
a.signal();
} finally {
awaitSignal.unlock();
}
}
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
class AwaitSignal extends ReentrantLock {
private int loopNumber;
public void print(String str, Condition condition, Condition next) {
for (int i = 0; i < loopNumber; i++) {
lock();
try {
condition.await();
System.out.print(str);
next.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}
}